A Use Case of Fine-tuning Llama-3.1-70B Model for Medical Diagnosis Based on LLaMA Factory
LLaMA Factory is an open-source low-code framework for fine-tuning large models. It integrates a wide range of fine-tuning technology widely used in the industry and supports no-code fine-tuning of large models via a Web UI. With more than 40,000 stars on GitHub, it has become one of the most popular fine-tuning frameworks in the open-source community. Based on the Llama-3.1-70B model, this use case demonstrates how to use the Aladdin platform and the LLaMA Factory training framework to complete model fine-tuning, enhancing Llama-3.1-70B’s professional capabilities in medical diagnosis and clinical decision-making, so that it can understand complex medical descriptions and generate diagnosis suggestions consistent with medical theory.
This use case adopts a multi-GPU parallel debugging solution specifically designed for large-scale model training workload, focusing on compute efficiency and horizontal scalability to fully address the challenges of highly complex training on large datasets. It supports elastic scaling, allowing resources to be adjusted on demand, and provides flexible pricing options to help users deploy efficiently, reduces costs, and maximizes compute ROI.
This use case is based on Aladdin v2.3.6. The operation interface may vary between versions. When using this use case, please refer to the interface of the version you have installed and adjust your operations accordingly.
Prerequisite
- You have already obtained an Alaya NeW enterprise account and password. You can click to complete quick registration.
- The current enterprise account has sufficient balance to meet your needs for using compute services. For additional details, please Contact US.
- You have already installed the Aladdin extension in the VS Code or Cursor code editor.
Preparation
Create Virtual Kubernetes Services (VKS)
In this use case, please follow these steps below to create VKS.
-
Sign in to the Alaya NeW platform with your registered enterprise account, select the [Products/Virtal Kubernetes Services] menu item, and click the “Add Cluster” button to open the “New cluster” creation page.
-
Configure the basic information, such as cluster name, description, and AI data center (AIDC). For this use case, the resource configuration of the cluster must meet at least these requirements in the following table. After completing the parameter configuration for adding VKS, click the
Activate Nowbutton to complete the creation process. You can view the created VKS on the [Product Center/Virtual Kubernetes Services] page. When VKS status is “Running”, it is ready for use. For more information, see Create Virtual Kubernetes Services. The VKS configuration of this use case is as follows.Configuration Item Requirement Description GPU H800 * 8 GPU type: H800 Storage 300GB - Image Repository 100GB Used to store image files and other data
Download the Model
All examples involving LLaMA Factory are demonstrated in an Aladdin Workshop. Follow these steps to create a Workshop are as follows.
-
In the VS Code Extensions panel, search for the Aladdin extension and install it. After installation, click the extension icon to open the login page, and Sign in to Aladdin using your registered enterprise account.
-
After logging in, return to the workspace, click
to open the configuration page for a new Workshop, and configure the parameters as shown in the figure below.
 info
info- Environment: For the runtime environment, select an image from the preconfigured
aladdin/llamafactorypublic image repository. - VKS: Select the Virtual Kubernetes Service you have created.
- PVC MOUNTS: For the mounted SubPath, enter the name of the folder you created under the file storage directory when VKS is created. For ContainerPath, enter
/workspace.
- Environment: For the runtime environment, select an image from the preconfigured
-
After completing the configuration, click “Submit”. In the new pop-up window (referred to as the remote page afterward), select "Linux". The remote page automatically installs the relevant plug-ins. When the remote Aladdin plug-in icon appears, the Workshop creation is complete.
-
Press
Ctrl+Shift+P(Windows/Linux) to open the Command Palette, choosePython: Select Interpreter, select the Python interpreter highlighted in the figure below, and then open the/workspace/folder.
-
Choose the [Terminal/New Terminal] menu item to open a terminal. In the terminal, run the following commands to configure the mirror address for the corresponding AIDC. The first command in the example figure below is for Beijing-Region-1. The seccond command is for viewing the model list for that AIDC. For more information on acceleration of model download, see the article Model Download Acceleration.
export HF_ENDPOINT=http://hfmirror.mas.zetyun.cn:8082
curl http://hfmirror.mas.zetyun.cn:8082/repos -
Run the following command to install
huggingface-hub, as highlighted by ① in the figure below.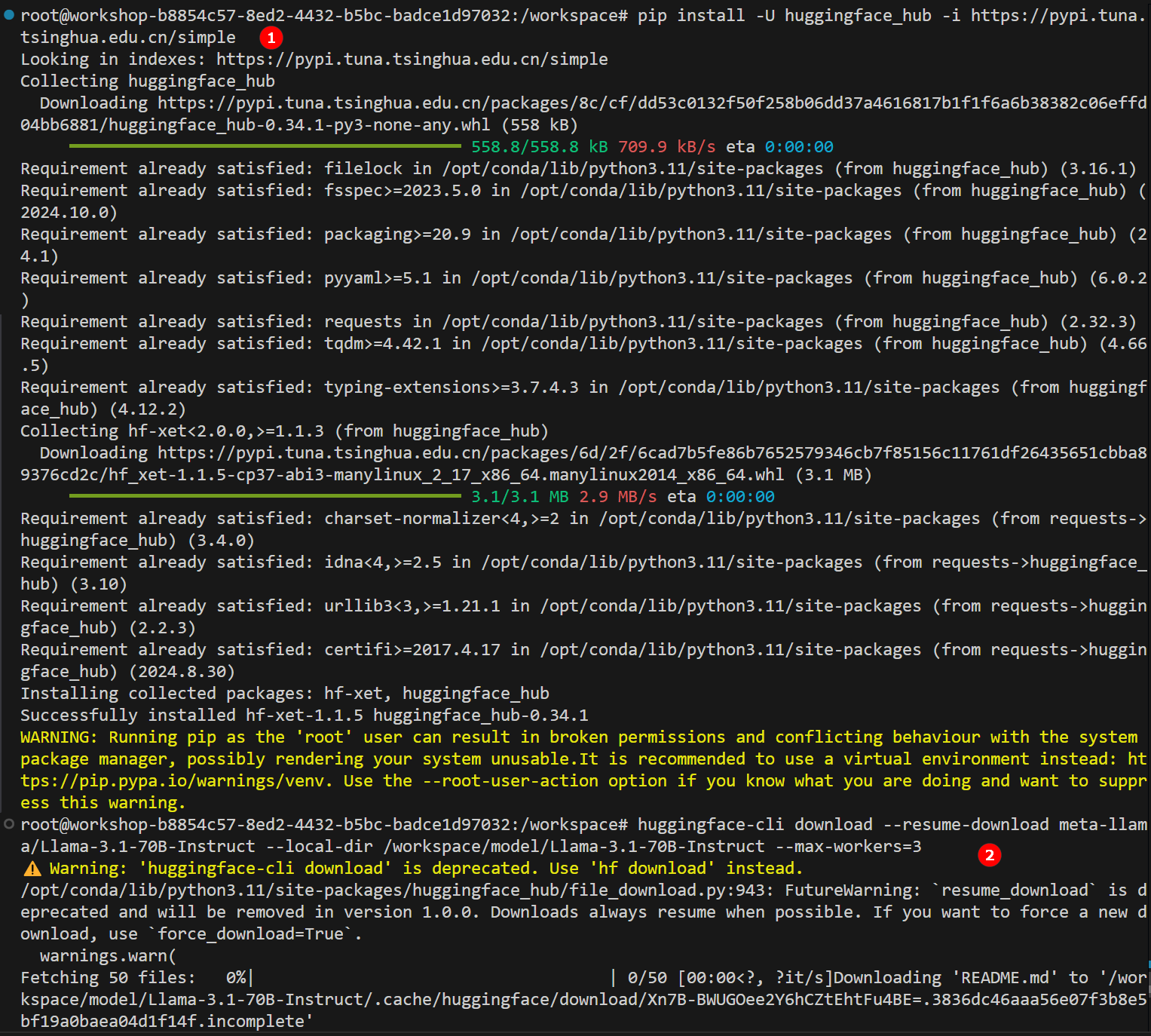
pip install -U huggingface_hub -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple -
Use the Hugging Face CLI to download the model meta-llama/Llama-3.1-70B-Instruct, as highlighted by ② in the figure above.
huggingface-cli download --resume-download meta-llama/Llama-3.1-70B-Instruct --local-dir /workspace/model/Llama-3.1-70B-Instruct --max-workers=3
Prepare LLaMA Factory
-
The environment selected when creating the Workshop already includes the LLaMA Factory source code. Therefore, you only need to copy the LLaMA Factory source code to the Workshop mount directory. The copy command is as follows, and an example page is shown in the figure below.
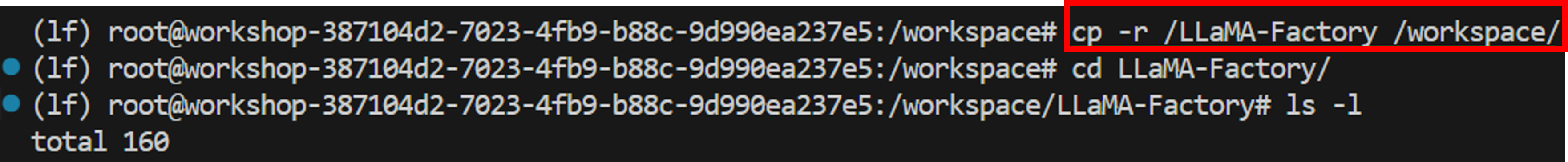
cp -r [source_code_directory] /[mount_directory] -
Click to download the Aladdin startup LLaMA Factory script files, extract the downloaded files locally, and drag final.sh and start.sh files into the LLaMA Factory source code folder. Then, in the directory in which these files are located, run the following commands.
chmod +x start.sh
chmod +x final.shtip- You need to update the LLaMA Factory source path in start.sh to the actual source path.
- You need to update the LLaMA Factory source path in final.sh to the actual source path.
Download the Dataset
-
Download the fine-tuning datasetand extract it locally. Drag the
jsonlfile into the "LLaMA Factory/data" folder。 -
Modify the "dataset_json.info" file in the "LLaMA Factory/data" folder, and add the following at the beginning of the JSON file.
"medical_sft": {
"file_name": "/workspace/LLaMA-Factory/data/medical_o1_sft_Chinese_alpaca_cot.jsonl",
"columns": {
"prompt": "prompt",
"response": "response"
}
}
Prepare the Visualization Tool
SwanLab is an open-source and lightweight tool for visualizing the track of AI model training. In this fine-tuning task, we will use SwanLab to record the full fine-tuning process. Before starting, make sure you have logged in to the SwanLab platform. After logging in, click “Settings/General“ to obtain the API Key, as shown in the figure below.

In the start.sh file, add the command line to install SwanLab, as shown below. The insertion location is illustrated in the figure.
pip install swanlab deepspeed==0.16.4 -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple/
Procedure
After completing the preparation steps, you can begin fine-tuning. The detailed steps are as follows.
-
In the
final.shfile editing view, right-click any empty area of the page and selectRun Shellfrom the pop-up menu, as shown below.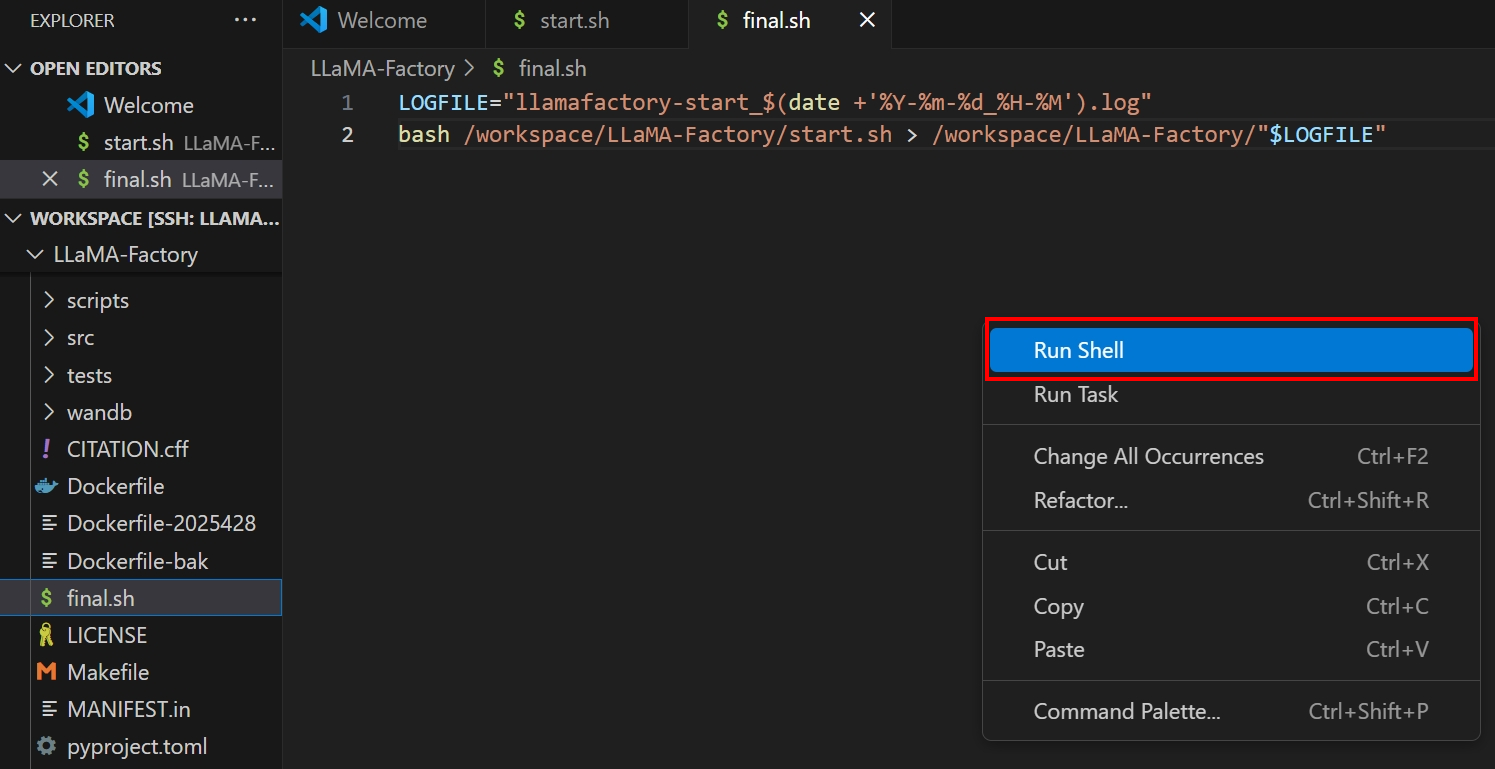
On the parameter configuration page, configure environment and resource parameters. In this use case, 8 GPUs are used, and the GPU type is selected as shown in the figure below.
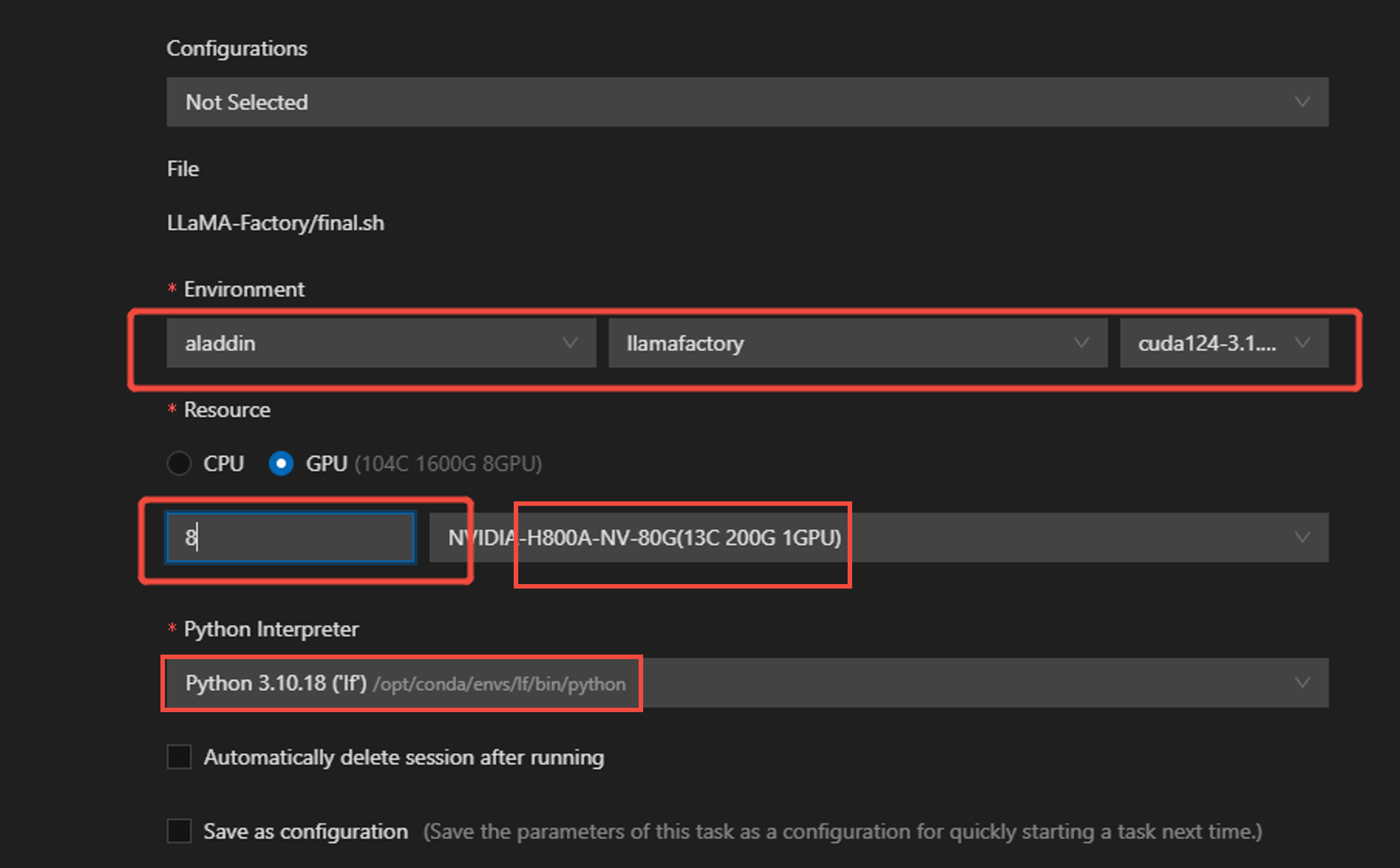
-
On the parameter configuration page, expand the “Advanced” settings, click “External Access” at the bottom to add an external access configuration, and enter port 7860 in the input field, as shown in the figure below.
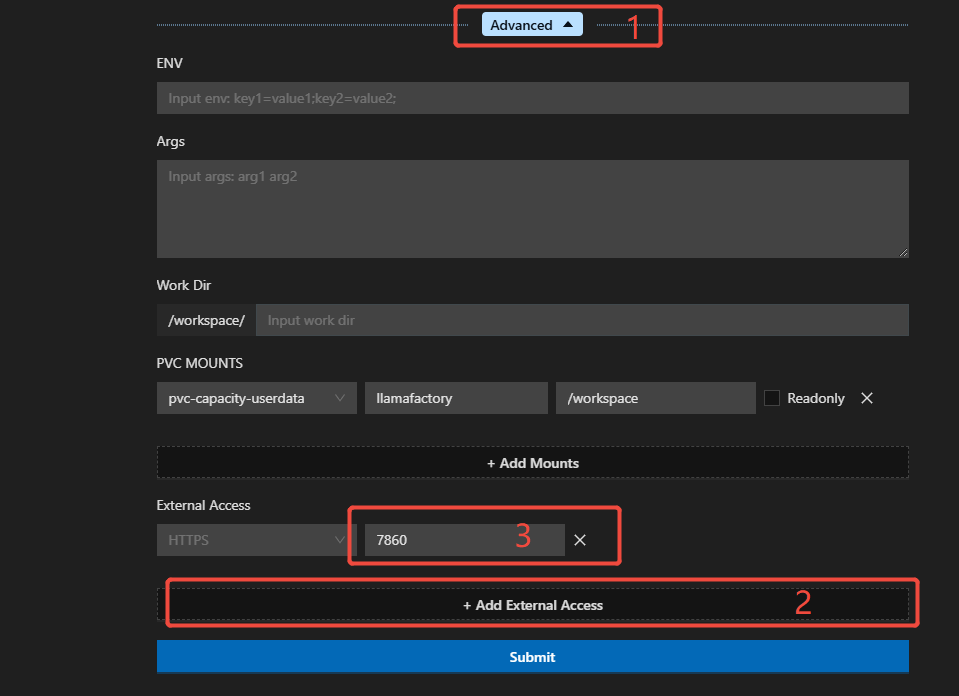
-
After the configuration is completed, click the “Submit” button and the system will create a develop session.
-
When the status indicator for external access turns green, click the arrow icon to access the application. In the pop-up window, choose “Open External Access to access the application via WebUI.

-
After entering the WebUI, as highlighted by ① in the figure, you can select the
LLama-3.1-70B-instruct model, as highlighted by ②. Keep the fine-tuning method with the defaultlora, which can greatly save GPU memory.
-
Use
medical_sftas the dataset, as highlighted by ④ above. Find theSwanLab parameter settingsmenu, check theUse SwanLaboption, and enter the API Key obtained in the preparation section in the SwanLab API key field, as highlighted by ⑤ above. -
Set
DeepSpeed Stageto3. Click “Preview command” to display all current configurations. If you want to run fine-tuning using code, you can copy this command and run it in the terminal. In this use case, WebUI is used for fine-tuning and click “Start” to start model fine-tuning. -
After fine-tuning begins, the log will appear at the bottom of the page. In SwanLab, you can view multiple charts under “Experiments”, as shown below.

At the same time, the fine-tuning progress and the loss curve will also be displayed. An example page after multiple rounds of fine-tuning is shown in the figure below. You can see that the loss values appear to flatten. When fine-tuning is completed, the output box displays “Training completed”.

-
After training is completed, in the WebUI select the path to the fine-tuned model in the checkpoint path field (as highlighted by “2” in the figure below), click the “Load model” button to load the fine-tuned model (as highlighted by “3”), then select the “chat” tab and use the loaded fine-tuned model for chat.

- Conversation with fine-tuned model
- Conversation with base model
- Enter the message you want to chat with the model in the dialog box at the bottom of the page, and click “Submit” button to send it. Observe the model’s reply. And you may find that the model after fine-tuning provide more specific and targeted response.


-
Clear the LoRA configuration in the “Checkpoint path” field, then click the “Load model” button to switch to the base
Llama-3.1-70B-Instructmodel. Enter the same question in the dialog box at the bottom of the page and observe the model’s reply. You will find that the base model can only provide common-sense or superficial suggestions and lacks deep reasoning ability.

Overall, after fine-tuning, the model provides more informative and valuable answers. Compared with the base model, which tends to provide broad and general descriptions, a model which is fine-tuned on a specific task or dataset can generate more precise and targeted output. Thus a model after fine-tune is better suited for real-world scenarios.
Summary
This use case demonstrates how to use Aladdin and the LLaMA Factory framework to efficiently fine-tune the Llama-3.1-70B model using the lightweight LoRA method, enabling it to understand complex medical descriptions and generate professional diagnostic suggestions. With powerful GPU resources and the VKS scheduling mechanism, training resources can be allocated with flexibility and scaled dynamically.
In real-world scenarios, users may purchse GPU compute on demand, with support for hourly billing and task-level resource allocation, significantly reducing idle costs and accelerating the entire process from model development to deployment. Whether for large-model inference or multimodal task fine-tuning, VKS can be used for rapid adaptation while balancing performance and flexibility.
Overall, the large-GPU fine-tuning solution based on VKS has the following advantages:
- Resource elasticity: Supports dynamic scaling by tasks and on-demand scheduling of multiple high-performance GPUs;
- Flexible payment terms: Supports short-term usage and pay-as-you-go, significantly lowering the barrier for enterprise compute;
- Higher efficiency: Multi-GPU parallelism and automatic container scheduling work together to significantly reduce fine-tuning time;
- Broad adaptability: Supports a wide range of model architectures and training tasks, making models better suited for rapid business deployment.
This solution provides a plug-and-play infrastructure for enterprise-grade AI applications, effectively supporting the end-to-end process from algorithm validation to product launch.